
- The Current Landscape of Outsourcing: A Cybersecurity Perspective
- Why Are Cybersecurity Audits Critical for Outsourcing?
- How Cybersecurity Audits Support Outsourcing in Regulated Industries
- Key Components of an Effective Cybersecurity Audit for Outsourcing
- The Future of Cybersecurity Audits in Outsourcing
- Conclusion
Outsourcing has become a critical strategy for improving efficiency, cutting costs, and accessing specialized expertise. However, with this growing trend comes the increasing risk of data breaches, cyberattacks, and regulatory compliance failures. For industries like healthcare and finance, where sensitive client data is at the core of operations, outsourcing demands an even greater focus on cybersecurity.
Data entry outsourcing can drive efficiency and cost savings, but safeguarding the data is crucial. Learn more about the benefits in our article on Data Entry Outsourcing
Cybersecurity audits are essential for ensuring the safety of client data when outsourcing back-office services. They offer a comprehensive evaluation of security policies, identify potential vulnerabilities, and ensure regulatory compliance. This blog explores why regular cybersecurity audits are indispensable for outsourced services, particularly in highly regulated sectors like healthcare and finance.
The Current Landscape of Outsourcing: A Cybersecurity Perspective
Outsourcing has expanded across industries, especially in sectors that deal with large volumes of sensitive data. The healthcare outsourcing market, for instance, is projected to reach $449.6 billion by 2028, driven by the need for efficiency in handling electronic health records (EHRs), medical billing, and insurance claims processing. Similarly, the financial services industry is increasingly outsourcing functions such as accounting, tax preparation, and payroll services to improve operational efficiency.
However, this rapid growth has been accompanied by a corresponding rise in cybersecurity risks. According to a report by Cybersecurity Ventures, cybercrime is expected to cost the world $10.5 trillion annually by 2025, and third-party vendors are frequently identified as weak links in the chain.
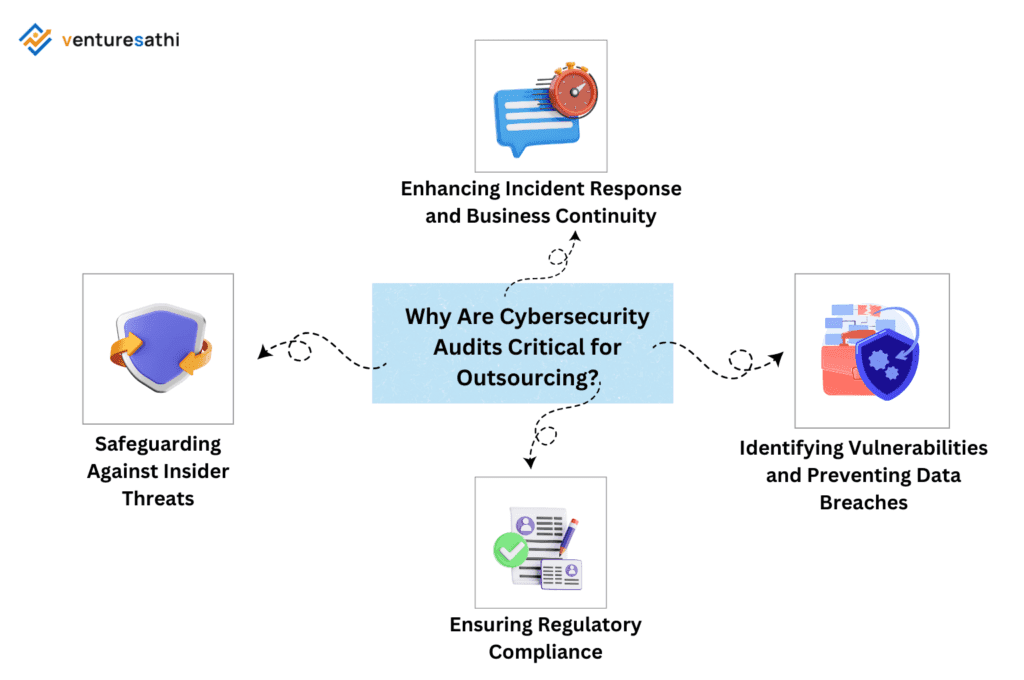
Why Are Cybersecurity Audits Critical for Outsourcing?
1. Ensuring Regulatory Compliance
Industries like healthcare and finance are governed by strict regulatory frameworks. Compliance with regulations such as HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) in healthcare and PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) in finance is non-negotiable.
Cybersecurity audits help ensure that outsourced vendors comply with these regulations by systematically evaluating their data protection practices. For example, a healthcare provider outsourcing medical billing services must ensure that the third-party vendor is HIPAA-compliant. A cybersecurity audit will assess whether the vendor has implemented the necessary safeguards, such as encryption, access controls, and regular employee training on data privacy.
2. Identifying Vulnerabilities and Preventing Data Breaches
Cyberattacks are becoming more sophisticated, and businesses must be proactive in identifying and mitigating risks. A cybersecurity audit provides a thorough evaluation of an organization’s IT infrastructure and processes, helping to identify potential vulnerabilities before they can be exploited by cybercriminals.
For example, audits may uncover weaknesses such as outdated software, weak access controls, or unencrypted data transmissions between the outsourcing provider and the client. Addressing these vulnerabilities early on can prevent data breaches that could result in significant financial and reputational damage.
3. Safeguarding Against Insider Threats
According to a report by Ponemon Institute, insider threats account for 60% of data breaches.
When businesses outsource back-office functions, they effectively expand the pool of individuals who have access to sensitive data, increasing the likelihood of an insider threat.
A cybersecurity audit evaluates the processes in place for managing insider threats, including employee background checks, access controls, and ongoing monitoring. It also ensures that vendors have implemented effective security awareness training programs to reduce the risk of human error or malicious insider activities.
4. Enhancing Incident Response and Business Continuity
A robust incident response plan is critical for minimizing the damage caused by a cyberattack. Regular cybersecurity audits evaluate how well an outsourcing provider is prepared to respond to an incident, including how quickly they can detect, contain, and recover from an attack.
Audits assess whether vendors have business continuity plans that account for cybersecurity threats, ensuring that client operations are minimally disrupted in the event of an attack. This is particularly important in industries like finance and healthcare, where even minor disruptions can have serious consequences.
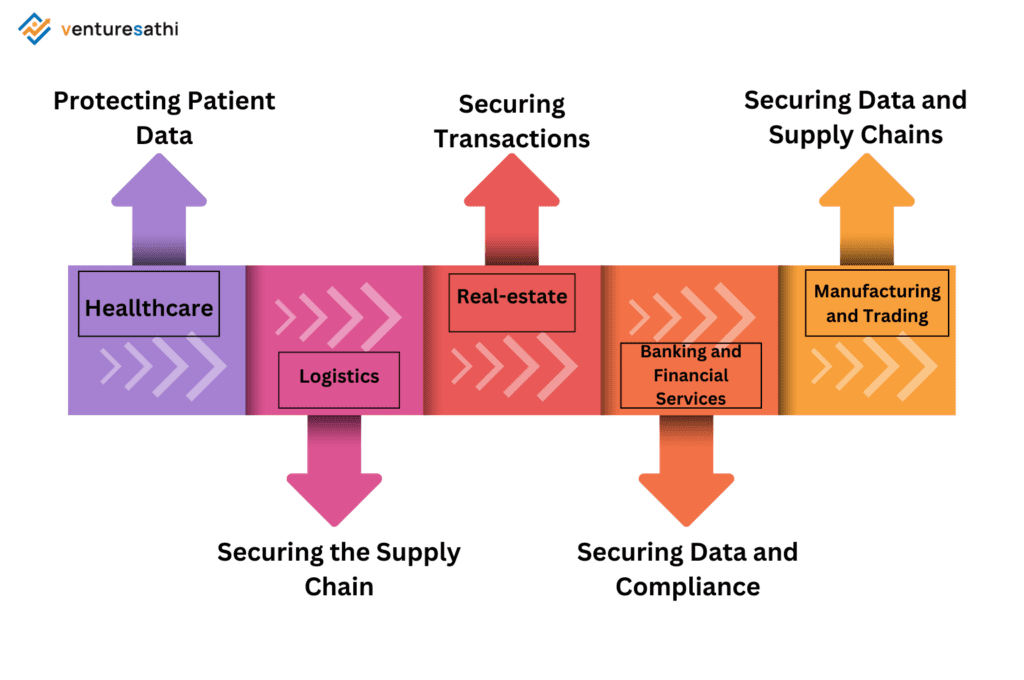
How Cybersecurity Audits Support Outsourcing in Regulated Industries
- Healthcare: Protecting Patient Data
In healthcare, the protection of personal health information is paramount. As electronic health records and telehealth services expand, cybersecurity audits help ensure that outsourced providers comply with HIPAA regulations, which include encryption, access controls, and breach notifications. With 93% of healthcare organizations experiencing data breaches, many involving third parties, regular audits can help close security gaps and avoid costly fines.
- Logistics: Securing the Supply Chain
The logistics industry increasingly relies on outsourcing for functions like supply chain management, making cybersecurity a critical concern. Cybersecurity audits ensure that security measures such as encryption and access controls are in place to safeguard the communication of sensitive data, particularly with the rise of IoT devices in shipment tracking.
- Real Estate: Securing Transactions
The real estate sector, which often handles sensitive client and financial information, is also turning to outsourcing for property management and transaction processing. Cybersecurity audits ensure compliance with regulations like GDPR, secure systems, and protect smart building technologies and digital twins.
- Banking and Financial Services: Securing Data and Compliance
In banking and financial services, outsourcing tasks like loan processing and asset management heightens data security risks. Cybersecurity audits ensure third-party compliance with regulations, verifying safeguards like encryption, access control, and response protocols. These audits help protect sensitive data, uphold compliance, and prevent reputational risks and penalties.
- Manufacturing and Trading: Securing Data and Supply Chains
In manufacturing and trading, outsourcing functions like supply chain management and inventory tracking exposes critical operational data to potential risks. Cybersecurity audits help ensure compliance with standards such as ISO 27001 by assessing encryption, network security, and access controls across third-party vendors. Regular audits protect sensitive data, maintain the integrity of interconnected supply chains, and minimize disruptions caused by cyber threats.
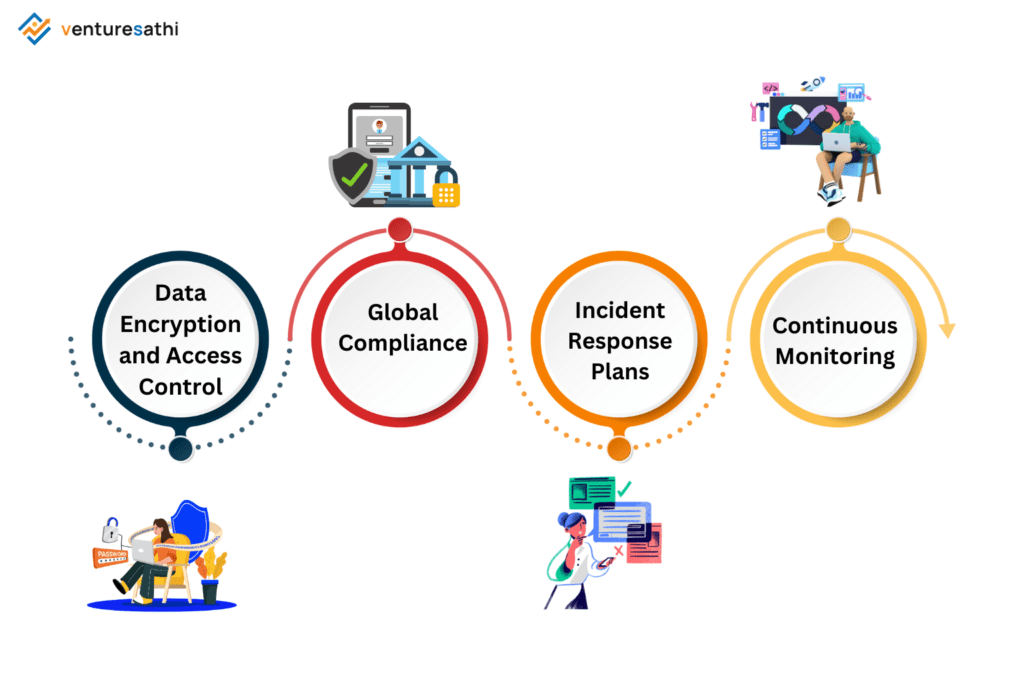
Key Components of an Effective Cybersecurity Audit for Outsourcing
- Data Encryption and Access Control
Cybersecurity audits ensure strong encryption methods are in place for both data in transit and at rest. Additionally, audits assess access controls, ensuring that only authorized personnel have access to sensitive information, using tools like role-based access controls and multifactor authentication.
- Global Compliance
For companies outsourcing across borders, compliance with international data protection standards like GDPR is critical. A cybersecurity audit confirms that vendors adhere to relevant global regulations, protecting them from legal repercussions and breaches.
- Incident Response Plans
Audits evaluate how well outsourcing providers respond to incidents, including how they handle breaches, notify stakeholders, and recover data. Regular audits ensure that incident response plans remain up to date with the latest cybersecurity threats.
- Continuous Monitoring
The evolving threat landscape requires continuous monitoring. Cybersecurity audits assess the ability of vendors to monitor systems and detect threats in real-time using tools like intrusion detection systems (IDS) and security information and event management (SIEM) systems.
Data Breaches and Outsourcing: Real-World Examples
Several high-profile data breaches have underscored the importance of robust cybersecurity in outsourcing.
In 2020, a major breach involving a third-party vendor affected 100 healthcare providers, exposing the personal health data of millions of patients.
Similarly, in the financial sector, a breach involving a payment processing firm led to the exposure of over 100 million credit card records, highlighting the need for better vendor risk management and stronger security protocols.
These incidents demonstrate that outsourcing can significantly increase the attack surface for cybercriminals. As more businesses turn to third-party providers, the potential for data breaches grows, necessitating a strong focus on cybersecurity audits to protect client data.
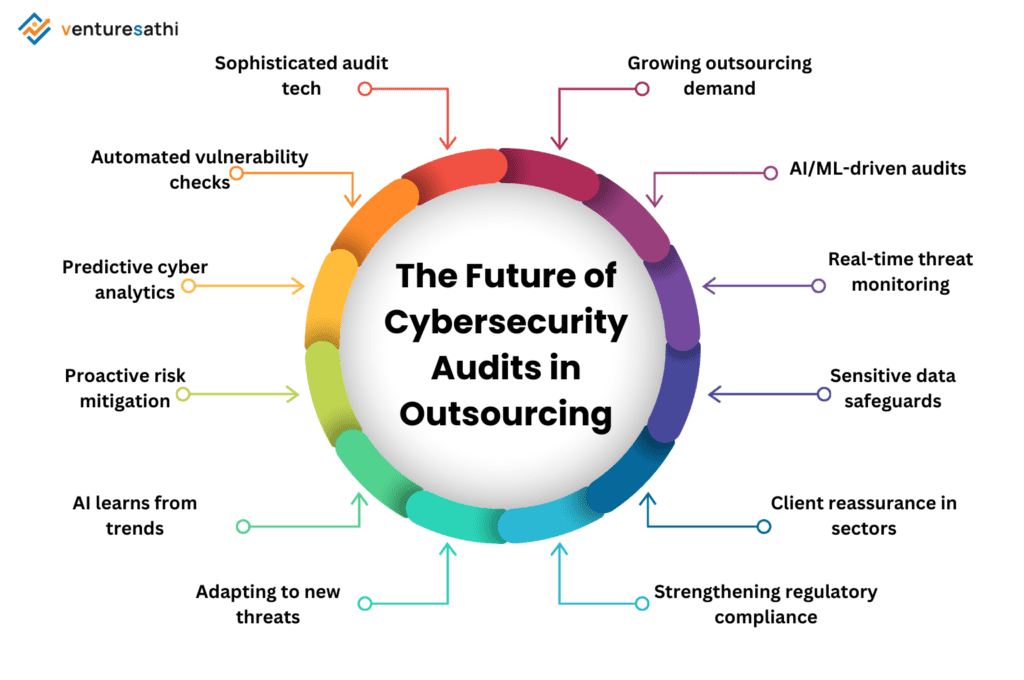
The Future of Cybersecurity Audits in Outsourcing
As businesses increasingly adopt outsourcing to streamline operations and access specialized expertise, the demand for regular and comprehensive cybersecurity audits has become essential. Outsourcing offers significant advantages, but it also introduces risks associated with data handling and access by external partners. With cyber threats evolving rapidly, organizations must ensure their outsourcing providers are equipped to safeguard sensitive data and maintain stringent security protocols within a constantly shifting threat landscape.
In the future, cybersecurity audits will not only grow in importance but also become more sophisticated, leveraging advanced technologies. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are anticipated to play a pivotal role in transforming the audit process. These technologies can automate vulnerability detection, analyze patterns in data breaches, and deliver insights that enhance the accuracy of risk assessments. Through automated, real-time monitoring, AI can help identify potential weaknesses more efficiently than traditional methods, minimizing the window for threats to exploit system vulnerabilities.
Furthermore, these technologies enable predictive analytics, allowing organizations to foresee potential cyber risks and mitigate them proactively. AI-based audit tools can learn from past incidents to identify emerging trends, thus adapting quickly to new cyber threats. This proactive approach to cybersecurity audits helps outsourcing partners uphold strict compliance with regulatory standards, reassuring clients in highly regulated sectors like healthcare and finance.
Conclusion
As businesses navigate the evolving cyber risk landscape, outsourcing partnerships that prioritize regular, technology-enhanced cybersecurity audits will stand out. Aligning with providers who leverage AI and ML in their security audits offers companies enhanced protection, fortifying defenses against cyber threats in a constantly changing digital world.
For outsourced back-office services, cybersecurity audits are essential to safeguarding sensitive client data and ensuring compliance with regulatory frameworks. Regular audits grant businesses confidence that their outsourcing partners are well-equipped to tackle security challenges effectively, mitigating risks before they escalate.
In highly regulated industries like healthcare and finance, where data security is paramount, investing in regular cybersecurity audits is not just best practice—it’s a necessity. By identifying vulnerabilities, strengthening incident response, and upholding regulatory compliance, these audits form the backbone of secure, successful outsourcing.


