- Importance of Data Security in Document Processing
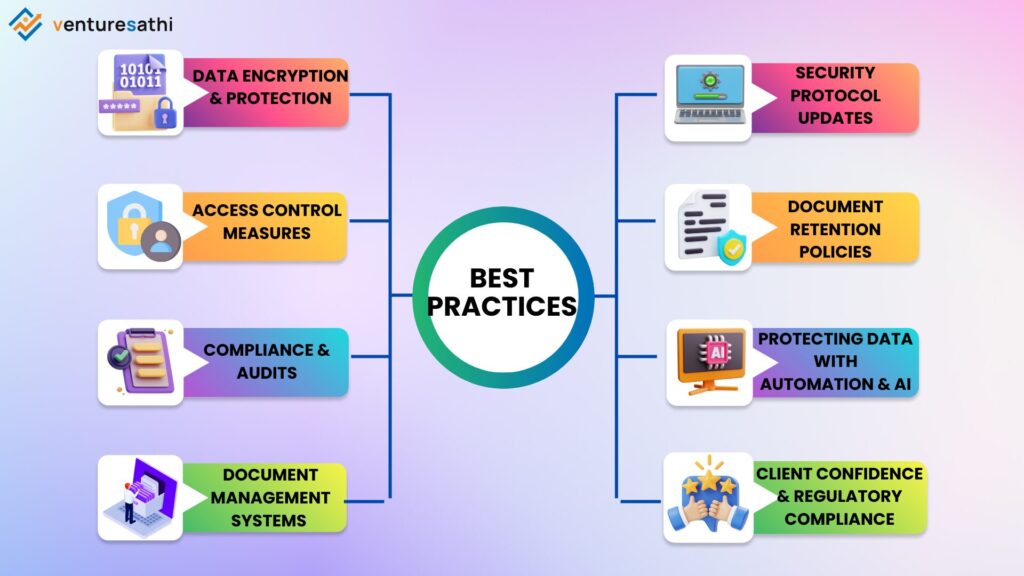
- Data Encryption and Protection
- Access Control Measures
- Compliance and Audits
- Document Management Systems (DMS)
- Regular Security Protocol Updates
- Document Retention Policies
- Protecting Data with Automation and AI
- Client Confidence and Regulatory Compliance
- Conclusion
The digital era has revolutionized how organizations handle documentation, emphasizing the critical need for data security. As digital processes enhance efficiency, they also expose businesses to the dangers of data breaches and unauthorized access. This guide explores key best practices for document processing security, offering strategies to protect sensitive data and foster client trust.
Importance of Data Security in Document Processing
Data breaches can devastate businesses, including significant financial loss, operational disruption, and irreparable reputational damage. The average cost of a data breach in 2023 was $4.45 million, with the United States experiencing an average cost of $9.48 million per breach (IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2023). In 2022, there were over 1,800 data breaches in the United States, exposing more than 422 million records (Identity Theft Resource Center).
The cost of a data breach extends beyond immediate financial losses, impacting customer trust and loyalty, and leading to long-term financial repercussions. Robust data security is crucial for maintaining client confidence, as clients expect their information to be handled with care and protected from unauthorized access. Implementing stringent security measures fosters trust and encourages long-term business relationships.
Data Encryption and Protection
Encrypting data both at rest and during transmission is crucial for protecting sensitive information. Data at rest, stored on devices or servers, should be encrypted to prevent unauthorized access. Similarly, encrypting data in transit, such as during file transfers or email communications, ensures that intercepted data remains unintelligible to unauthorized parties.
In 2022, 50% of organizations extensively used encryption across their enterprises (Ponemon Institute: 2022 Global Encryption Trends Study). Encryption can reduce the cost of a data breach by an average of $1.25 million (IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2023). Common protocols like HTTPS and SSL/TLS are essential for securing data transmissions, and safeguarding against eavesdropping and tampering.
Access Control Measures
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) is a security approach that limits access based on users’ roles within the organization. By assigning permissions according to job responsibilities, RBAC minimizes the risk of unauthorized access and ensures that employees only have access to the information necessary for their roles.
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) enhances security by requiring users to verify their identity through multiple authentication methods, such as passwords, biometrics, or one-time codes. Implementing MFA can block 99.9% of automated attacks (Microsoft Security Blog). Approximately 57% of enterprises had implemented MFA by the end of 2022 (Duo Security). This additional layer of security significantly reduces the likelihood of unauthorized access, even if one authentication factor is compromised.
Regular access control audits are essential to identify outdated permissions and unauthorized access, keeping security measures up-to-date and aligned with organizational roles.
Compliance and Audits
Organizations must comply with various data protection regulations, such as GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA, which mandate stringent data security measures. These regulations protect personal data and ensure that organizations handle information responsibly.
Regular compliance audits are critical for verifying adherence to regulatory requirements. These audits assess the effectiveness of security measures, identify areas for improvement, and ensure that organizations remain compliant with evolving data protection laws.
Training staff on data security and compliance is vital for fostering a security-conscious culture. Regular training sessions educate employees about potential threats, safe data handling practices, and the importance of adhering to security protocols.
Document Management Systems (DMS)
Document Management Systems (DMS) offer robust security features that help manage access and ensure document security. Around 78% of organizations use some form of DMS to manage their documents and ensure security. DMS solutions provide centralized storage, access control, and encryption, safeguarding documents against unauthorized access and tampering.
Automated backups are a critical feature of DMS solutions, ensuring that documents are regularly backed up and can be restored in case of data loss. Regular backups protect against data breaches, system failures, and other disruptions.
DMS solutions often include audit trail capabilities, which track document access and modifications. Audit trails provide a transparent record of who accessed what documents and when enhancing accountability and security.
Regular Security Protocol Updates
Staying ahead of emerging security threats is essential for protecting sensitive information. Cyber threats are constantly evolving, and organizations must be proactive in identifying and mitigating new vulnerabilities.
Timely updates and patch management are crucial for addressing security vulnerabilities. Regularly updating software, operating systems, and security protocols ensures that the latest protections are in place to defend against potential attacks.
Conducting regular risk assessments helps identify and address vulnerabilities within an organization’s security infrastructure. Risk assessments evaluate the effectiveness of current security measures and provide insights into areas requiring improvement.
Document Retention Policies
Implementing document retention policies is essential for managing the lifecycle of documents. Proper retention and secure disposal practices reduce the risk of data breaches and ensure compliance with legal requirements. Proper retention and disposal practices reduce the risk of data breaches by 30% (Ponemon Institute: Data Retention and Disposal Practices Study).
Retention policies help organizations comply with legal and regulatory requirements regarding data retention. These policies ensure that documents are retained for the necessary duration and securely disposed of when no longer needed.
Effective retention policies streamline information retrieval, reducing storage costs and enhancing operational efficiency. Organized retention schedules ensure that documents are easily accessible when needed.
Protecting Data with Automation and AI
Automation reduces the risk of human error in data handling by 50% (McKinsey & Company: The Future of Work). Automated processes ensure consistency, accuracy, and adherence to security protocols, minimizing potential mistakes that could compromise data security.
AI technologies enhance processing speeds and efficiency, allowing organizations to manage large volumes of data quickly and securely. AI and automation in data processing can increase efficiency by up to 80% (Deloitte Insights: AI and the Future of Work).
AI-driven tools can automate tasks such as data classification, encryption, and threat detection. Automated systems provide consistent and accurate data handling, ensuring that security protocols are uniformly applied across all documents. This consistency enhances overall data security and reduces the risk of unauthorized access.
Client Confidence and Regulatory Compliance
Robust data security practices build client trust by demonstrating a commitment to protecting sensitive information. Clients are more likely to engage with organizations that prioritize data security and take proactive measures to safeguard their data. 84% of consumers say they would be more loyal to companies that have robust data security measures in place (PwC Consumer Intelligence Series).
Compliance with data privacy regulations is essential for avoiding legal penalties and maintaining operational integrity. Adhering to regulatory requirements demonstrates a commitment to responsible data handling and protects organizations from legal repercussions. Companies that experience a data breach see an average decline of 5.4% in customer trust (Cisco 2023 Data Privacy Benchmark Study)
Strong data security practices provide a competitive edge by differentiating organizations in the marketplace. Clients prioritize working with companies that prioritize data security, making it a valuable selling point.
Conclusion
Ensuring data security in document processing is not just a technical concern but a critical business strategy. Implementing best practices like data encryption, access control, regular audits, and robust document management systems enhances data security. Staying proactive against threats, conducting risk assessments, and cultivating a security-focused culture safeguard sensitive information, uphold client trust, and ensure compliance with regulations. These strategies not only protect your data but also give you an edge in the modern digital environment.